
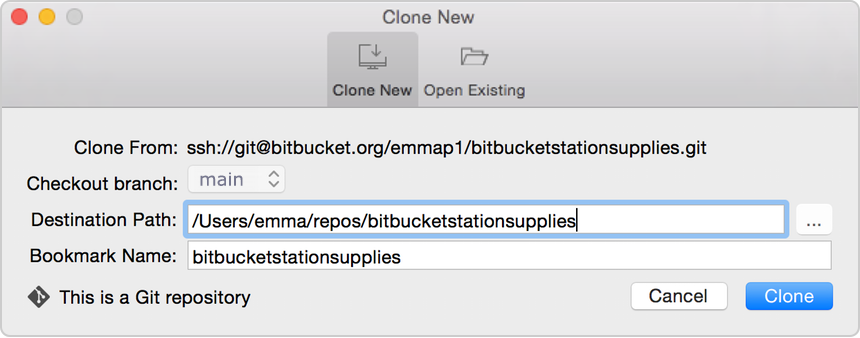
If you choose to clone with SSH, you would use a specific SSH path for the repository instead of a URL. git clone With SSHĭepending on how you authenticate with the remote server, you may choose to clone using SSH. The recommended solution is to optimize the performance of the repository before relying on single branch cloning strategies. Git clone -branch -single-branchĬloning only one branch does not add any benefits unless the repository is very large and contains binary files that slow down the performance of the repository. You can specify a certain branch to clone, but the default branch, usually main, will be selected by default. This means no other branches will be cloned. This will create a clone that only has commits included in the current line of history. Both of these things happen when you use -single-branch with git clone. The only local branch that is created is the default branch.īut, maybe for some reason you would like to only get a remote tracking branch for one specific branch, or clone one branch which isn't the default branch. Git clone -single-branch: By default, git clone will create remote tracking branches for all of the branches currently present in the remote which is being cloned. This is only done once, when you begin working on a project, and would follow the syntax of git clone. The most common usage of cloning is to simply clone a repository.
You can see all of the many options with git clone in git-scm's documentation. This may be a good option if you are cloning a repository that you know to have submodules, and you will be working with those submodules as dependencies in your local development. `git clone -recurse-submodules: After the clone is created, initialize and clone submodules within based on the provided pathspec.This could help with performance when cloning large repositories with many directories and sub-directories. git clone -sparse: Instead of populating the working directory with all of the files in the current commit recursively, only populate the files present in the root directory.git clone -single-branch: Clone only a single branch.This may occur during configuration using a new remote for your Git hosting, or when using Git during automated testing. You may want to use this if you are trying to create a secondary copy of a repository on a separate remote and you want to match all of the branches. git clone -mirror: Clone a repository but without the ability to edit any of the files.
#How to clone in gitlab for mac how to#
How to Use git clone Common usages and options for git clone

Once you have cloned a repository, you won't need to clone it again to do regular development. Once a repository already exists on a remote, like on GitHub, then you would clone that repository so you could interact with it locally. By cloning with Git, you get the entire repository - all files, all branches, and all commits.Ĭloning a repository is typically only done once, at the beginning of your interaction with a project.
#How to clone in gitlab for mac update#
This saves you from having to manually initialize and update the submodules later.When you clone a repository, you don't get one file, like you may in other centralized version control systems. If your project contains submodules, using this parameter will make sure that all submodules will both be cloned and initialized once the main project has been cloned. recurse-submodulesĬlones and initializes all contained submodules. If this option is not specified, Git will simply create a new folder named after the remote repository. The name of the folder on your local machine where the repository will be downloaded into. Usually, this will point to a remote server, using a protocol like HTTP, HTTPS, SSH, or GIT. Specifies the URL of the remote repository. That remote repository's URL is then later referred to as the "origin". Typically, the "original" repository is located on a remote server, often from a service like GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab). You will then have a full-blown, local version of that Git repo and can start working on the project. The "clone" command downloads an existing Git repository to your local computer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
